
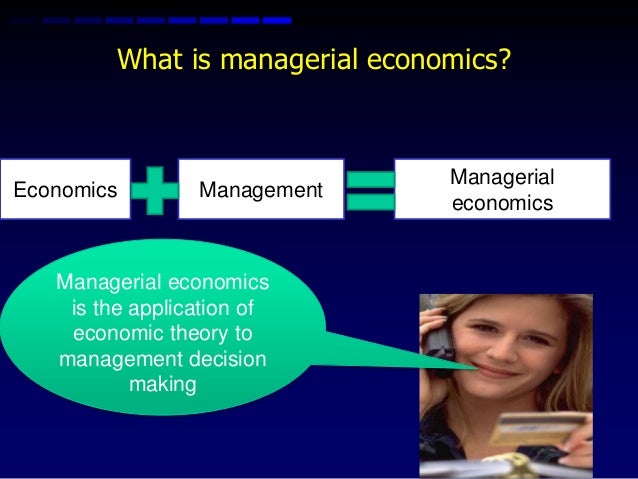

The main production activities in a traditional economy include farming, pastoral activities, and hunting. A traditional economy will most definitely rely on customs of inheritance and base their production of goods on how the previous generations have carried out their production activities. Traditional economics relies on the use of old cultures, trends and customs in allocating scarce resources to obtain a benefit. Traditional economics refers to the more primitive principles of modern economics that are most commonly used in underdeveloped countries that have not yet embraced the rapid technological and globalization changes that have occurred in the study of economics over the years. Managerial economics also helps managers decide which products to produce, how much to produce, prices to be set, and channels to use in the sales and distribution. Managerial economics helps managers make the right decisions in the allocation of scarce resources such as land, labour, capital to achieve the highest profitability while minimizing costs. Managerial economics makes the use of mathematics, statistics, management theories, economic data and modelling techniques in order to help business managers to carry out their operations with maximum efficiency. Managerial economics refers to the branch of economics that is derived from the subject matter of microeconomics that considers the households and firms in an economy, and macroeconomics that is concerned with the employment rates, interest rates, inflation rates and other macroeconomic variables that concerns a country as a whole. The following article clearly explains the difference between economics and managerial economics. Managerial economics is based on both microeconomics and macroeconomics, whereas traditional economics refers to the concept of economics that is more traditional and primitive in nature. The theory of economics in today’s world is a broad subject which is divided into microeconomics and macroeconomics. Economics is social science that is concerned with the production of goods and services, distribution and consumption of those goods and services, and transfer of wealth between entities within a country or across regions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
